The California-based multinational technology giant, Intel, has been leading the microprocessor market for as long as most can remember. However, Intel don’t only deal in microprocessors – they manufacture motherboards and a number of other peripherals as well.
Maintaining high standards that led the company to the top position in the market, Intel is present in pretty much every home and business nowadays, whether you are aware of it or not.
With computers being more and more present in people’s lives, manufacturers hit, year after year, new records in sales. Adding up to the demands of the business world, ever-so-developing and their necessities, home desktops and laptops reached a whole new level with the advent of online gaming.
By supplying outstanding quality components for both worlds, Intel has kept their lofty status in the manufacturing of computer parts.
In addition to the excellent quality of its products, Intel also invests heavily in further development and performance, delivering features and functionalities that enhance users’ experiences to a greater extent.
Alongside the top-notch quality and the features, their products also reign over the compatibility kingdom, allowing users’ experiences to achieve an undreamt-of level of immersion and performance.
Regarding the internet world, Intel has put its best efforts into designing the top echelons of adapters, ethernet boards, network equipment, amongst other gear.
As per the performance and experience enhancers, Intel’s software optimization features increase the control over networks and allows users who seek higher speeds to share connections.
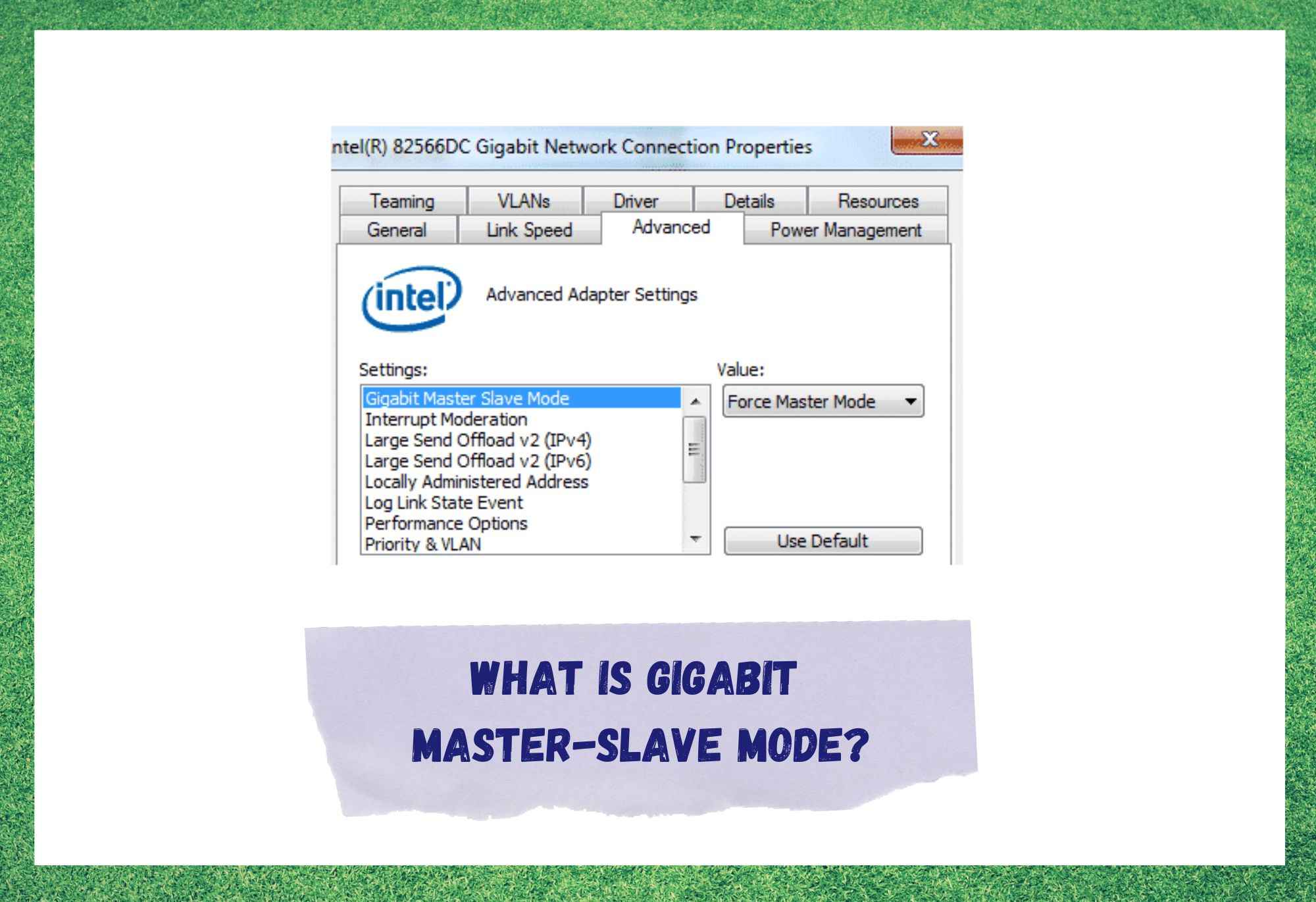
A good example of an experience and performance enhancer is the Gigabit Master-Slave Mode, which was recently announced by the company and promises to bring in a whole new era of the virtual world.
What is Gigabit Master-Slave Mode? (Explained)
As mentioned before, the Gigabit Master-Slave Mode promises a new revolution in the way people connect to the internet. This exclusivity of Intel cards, serves as a controller that will put the reins of many internet features and resources in the palm of your hand.
As it works with almost all of the Intel ethernet adapters, many users will be able to enjoy its functionalities and get the most out of their internet connections.
Apart from working as a driver for the network components, its options range from changing the name of your network all the way through the router options until deciding which end of the connection will determine the speed.
By enabling the Gigabit Master-Slave Mode, users will be able to choose which side of a connection will determine the speed of the data traffic.
Although that seems very futuristic, Intel has already cranked up the internet speed game and brought their customers this magnificent feature. Before we get into more tech-savvy details, let us explain a few things as not everyone is not so up to date with the current tech lingo.
As it goes, every time we connect to the internet, data is being transferred from both sides. In more mundane language, on one side we have our adapter and on the other, the link we are accessing.
During the time you are visiting a webpage or streaming an episode of your favourite series, for example, data is in constant exchange. In order to make it even more plain, our adapters are called ‘sender’ and the link, ‘receiver’, which Intel changed to master and slave to facilitate the control.
Normally, the speed of our internet connection is determined by our adapters, but with Gigabit Master-Slave Mode users can opt to use the connection of the link, or slave. That means, if you are visiting a link that has better internet speed, you can make it your master connecting device, thus enjoying higher speeds.
You will need both ends to be compatible to that mode, as the feature is not pre-loaded on most ethernet cards. As more and more computers have this feature, it will become more common for users to ‘share’ the control over internet speeds.
What Is The Forced Master Mode?
Gigabit Master-Slave Mode also offers a different mode that ensures one of the sides will automatically be set as the master. That is the Forced Master Mode, and it will set up one of the ends as the master once the connection is established.
Under optimal conditions, that is to say when internet connections are working as they should, the software controller will determine who is the master and the slave or, if commanded to, prompt the user to select which end of the connection will be the master.
In order for that to happen, it is required that both sides have the feature, or one of them has the chance to take over and cause the other to suffer a considerable drop on connection speed.
Should it happen that one of the ends does not have the Gigabit Master-Slave Mode feature, or has not enabled it yet, an attempt to use the forced master mode may result in internet connection losses or a force-down to 100Mbps on the link, or slave.
Additionally, on most multiport devices, the master mode will not work unless the Forced Master mode is enabled. Consequently, should the forced slave mode not be enabled, the same result may be expected.
The best idea is to use the Gigabit Master-Slave Mode only when both devices have the feature enabled. That way users can be sure to only enhance their internet speeds, and none will be sacrificed.
So, go ahead and enable the Gigabit Master-Slave Mode feature on your system and get the most out of your network link’s potential. In order to access and activate the Gigabit Master-Slave Mode, users should go to the advanced network settings on the network assistant.
On a final note, should you find out about other features of the Gigabit Master-Slave Mode, make sure to leave us a comment. By doing so, you will be helping our fellow readers get the most out of their internet connections.




