Long gone are the days when we needed a dial-up or simple DSL connection to connect to the internet and there were no other choices either. With the passage of time and development of technology, there are tons of new features being introduced that make getting things easier. Bridging is one such technology that allows you to connect two or more devices or modems together to pool in their resources and get the best out of it. To understand the concept better, let’s have a look at Transparent bridging and difference between tagged vs untagged:
Transparent Bridging Tagged vs Untagged
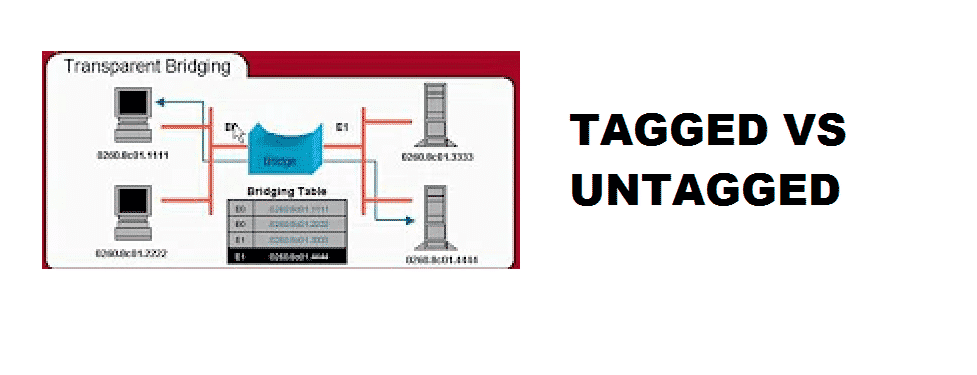
Transparent Bridging
Transparent Bridging is normally used to learn and keep track of all the MAC addresses of all nodes and their associated ports. This helps filter the incoming frames and data from their originated ports to the destination ports through the associated port on the bridge. The technology is mostly used in VLAN networks to ensure more stable and better connectivity. Now, tagged Vs. untagged transparent is an extensive topic that requires some detailed elaboration in the technical terminologies. To get a better idea of the differences between these two, you need to have a look at the following:
Tagged
In the most basic terms, a tagged transparent bridging allows the network traffic to pass for multiple VLANs. To get it simpler, a tagged port also known as the trunked port is used to link switches. With that being said, you need to understand that a network usually consists of two types of devices and ports. There are generally some links and ports on a bridged network that are used to connect more ports and connections and then there are end devices.
If you are intending to use a port for it to be connected to other devices and use it as a medium for bridging on the network, you need to ensure that the port is tagged. It will allow network traffic for multiple devices to transfer on that designated port and you will be able to connect as many devices as the traffic is not routed to a single port that is for the end device but switches.
Untagged
Untagged or Access ports are usually ports that would accept traffic for a single VLAN. These ports are usually used for transparent bridging to identify those devices that are end devices such as your PCs, smart TVs, or laptops. With the untagged option on these ports, traffic that is dedicated to such devices is not being transmitted over the whole network to ensure faster connectivity and no lags at all.
Untagged ports on end devices are just like a restriction that the data that is being transmitted to or from these devices is not distributed over the rest of the network bridge and cause some errors with the traffic. This is a great innovation that helps bridging over VLAN more fun and convenient for all types of users.
If you are wondering which of them you should be using for the network that you are trying to bridge, it all depends on the devices and switches that you are using for the network. You can use these both together on a network for each specific port associated with the switch or end device, but you should be sure about the correct MAC address to apply the right type of transparent bridging to it.
Be mindful that if not selected the right type, your network can cause some errors or even stop working at all due to obvious reasons. Hence, you need to ensure that you have a clear outlook of your network at hand before attempting to access these settings and have a clear and better idea about both the technologies and how they work. The best practice would be to configure both sides of a link identically to have the network work optimally. If for some reason, they are not identical on both sides, the link might work just fine but can cause troubles out of nowhere and that gets pretty had to diagnose and troubleshoot.