What Is Coaxial Cable?
Coaxial cable or Coax cable is a thick copper cable outfitted with metal shielding around as well as the other protective components to prevent signals interference. Coax cable is used to transmit Radio Frequency (RF) signals from point to point.
Coaxial cable had been named like this, and it is because of the fact that one of this cable’s physical channel is carrying the surrounded signal right after an insulating layer by the second coextensive physical channel. Both of them run along the same axis. Thus it makes it coaxial cable.
However, an outer channel acts as a ground. Coaxial cables carry vast information for a considerable distance as numerous coaxial tubes are situated inside the single sheathing (outer) along with the repeaters themselves.
Most of the TV companies use this cable to establish a direct connection with their satellite antennas facilities to consumers’ homes and workplaces. Often, telephone companies use coax cable to have a relationship between central offices and the telephonic poles nearby the consumers. Additionally, it is extensively used as an application for an “Ethernet” connectivity medium.
The technology of Coaxial cable has been around for more than a century serving as a medium to establish a firm connection with a satellite antenna.
How Does Coaxial Cable Look?
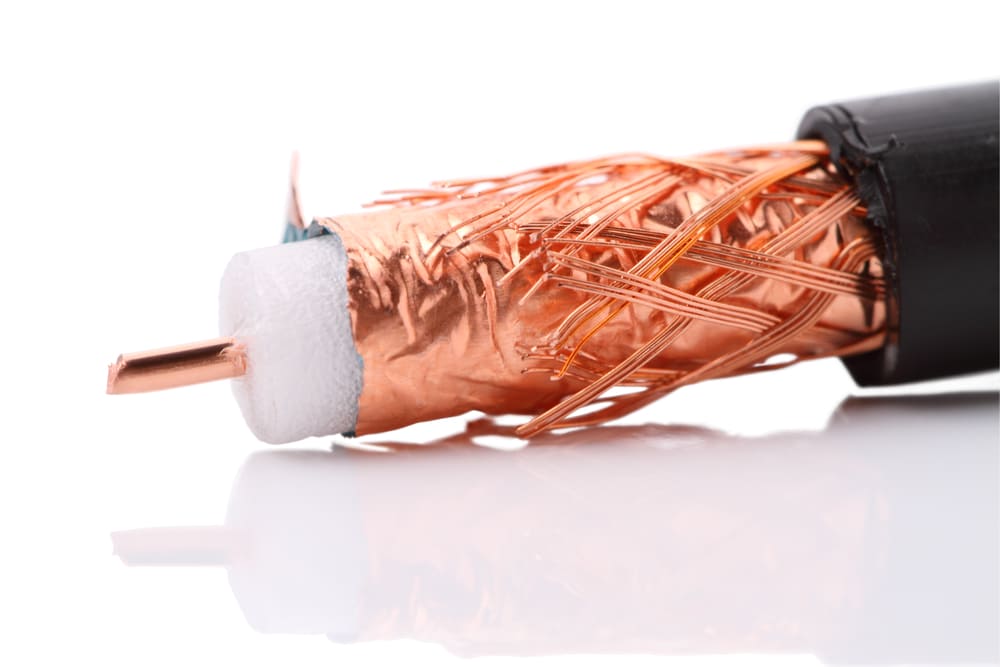
Coaxial cable has got a thick distinct round-shaped body outfitted with an interior insulating layer. The size of the coaxial cable makes it appear comparatively distant to other cable types, i.e., twisted pair.
Coaxial cable has four distinct parts. Its first part is rounded and precisely cylindrical. The second part is comprising of a thick layer of insulating plastic and some kind of non-conductor. The third structured part is thin-layered metal jackets, carrying signals. Finally, the fourth part, which is the exterior layer, thick plastic, built for the protection of interior metal jacketing.
How Does Coaxial Cable Work?
Coaxial cables are the most preferred cables since they are equipped with a super protective shielded design, which allows fast data transmission without having to face any damage and unexpected interference.
For a better understanding of working of coaxial cable, one has to comprehend the functions of these cables’ four built-in layers:
- The central part of a cable, which is mainly a copper wire, is used to let data travel within the wire.
- The central copper wire is surrounded by dielectric plastic insulation.
- A fine braided mesh of copper prevents electromagnetic Interference (EMI).
- While the external layer, which is a plastic coating, serves as a protection to prevent damage to the internal layer.
Thus, coaxial cable functions by carrying data in the central conductor, while the surrounding layers shields stop the signal loss and help to reduce EMI. Dielectric or the first layer serves as a distancing medium between the core conductor, the outer layers, and the insulation.
Moreover, the next layers serve as shielding layers are, keep the radio transmission and electrical impulses stay out.
What Are The Types Of Coaxial Cable?
Few main types of the coaxial cables are discussed down here:
Hard-line coaxial cable:
These coaxial cables rely on rounded copper tubes as well as a combination of metals that perform shielding made up of aluminum or copper. These cables establish the connection of a transmitter and an antenna.
Tri-axial cable
These cables are equipped with the third layer shielding, grounded for the protection of signals transmitting down the cable.
Rigid-line coaxial cables
These coaxial cables are created with a pair of copper tubes, functioning as an unbendable pipe. They are mostly designed for indoor applications that utilize high-power radio frequency transmitters.
Radiating cable
These cable mimics might have the components of hard-line cables. However, they have the tuned slots in their shields suitable for the RF wavelength. These cables are abundantly used in military equipment, elevators, and underground tunnels.
Coaxial Cable For Internet:
The coaxial cable that is extensively used for the internet is RG-6 Coaxial Cable. These RG-6 coaxial cables are used in carrying signals for internet connections since internet signals run at much higher frequencies other than traditional analog video frequencies.
In this way, RG-6 cable was designed for the fulfillment of the mentioned requirement. RG-6 coaxial cables have a larger conductor, which serves a capacity for much improved and better signal quality, along with that, the dielectric insulation is comparatively much thicker. These RG-6 cables are equipped with extensively different kinds of shields, which pretty much explains that these cables have the potential to carry GHz level signals much more effectively and efficiently.
However, most of the RG-6 has made it mandatory to use braided a foil as a shielding material. Though the braid has looser weaves (e.g., 60% versus the 90%+ of RG59), however, most of the RG6 cables require the use of high-percentage twist to function efficiently.
Some highlighted features of RG-6 coaxial cable are:
- Compatibility with almost every home-electronics.
- Fewer chances for signal loss.
- Excellent picture resolution and quality with no distortion.
- Impressive evidence rate of 75 Ohm.
- PVC jacketing guarantees waterproofing quality.
- Connectors are virtually non-destructible.
- Transmission range of 2.3MHz to 3.0MHz.
- Length variation of 3 feet-100+ feet.
What Is The Transmission Speed Of Coaxial Cable?
Coaxial cable has got an impressive transmission speed of about 10Mbps (megabits per second), which has the potential of providing 80 times more transmission capacity as compared to other network cables, i.e., twisted pair cable.
What Are The Pros And Cons Of Coaxial Cable?
Pros:
- Coaxial cables are inexpensive and readily available.
- Installation of coaxial cable and its wiring is simple.
- Coaxial cable is easily expandable.
- It has excellent resistance to EMI.
- Coaxial cables have a capacity of about 10Mbps.
- Coaxial cables are durable and robust.
Cons:
However, functioning with coaxial cable can get to one’s nerves when the failure of a single cable potentially suppresses an entire network and take it down with itself.
Though the substitutes used for the coaxial cables are twisted pair cable and fiber optic cable based on the crafted carrier technology and usage of some other factors.